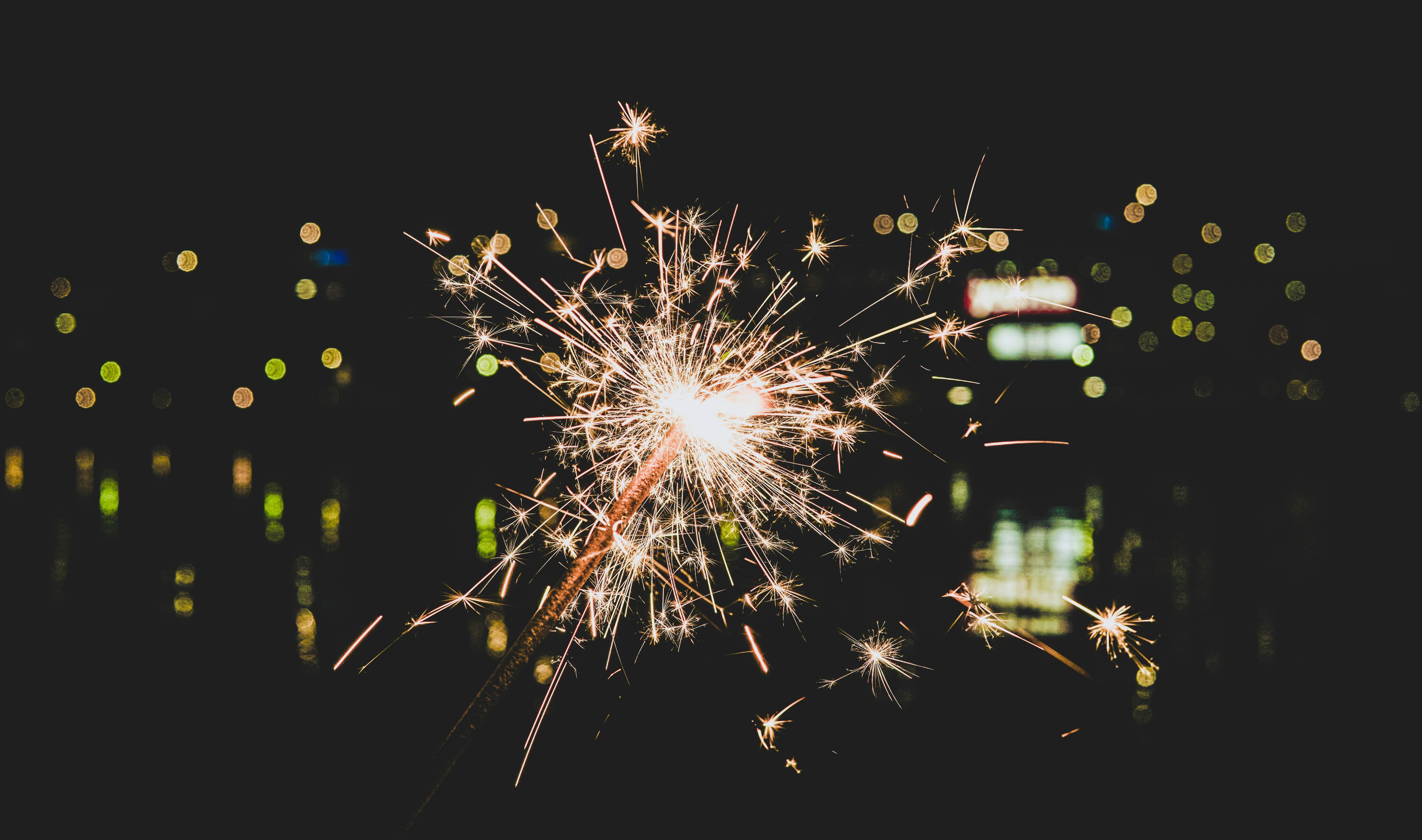
Japan’s Hanabi Taikai (Fireworks Festivals) are an annual summer highlight, drawing countless enthusiasts, families, and tourists to witness breathtaking fireworks displays against the night sky. Held throughout Japan from July to August, these festivals embody the spirit of Japanese summer, combining tradition, art, and a sense of communal celebration. Fireworks in Japan aren’t merely for entertainment; they are symbols of beauty, tradition, and even spiritual reverence, deeply embedded in Japanese culture.
The origins of Hanabi Taikai date back to the Edo period (1603-1868), where fireworks displays began not only as entertainment but also as a way to honor the spirits of the dead and pray for peace. During those times, Japan suffered from famines, disease, and other hardships, and fireworks were used to offer hope and express resilience. While originally tied to religious and ceremonial events, over time, fireworks festivals transformed into popular summer events for people of all ages.
In modern Japan, fireworks festivals are more than visual spectacles; they’re also social and family gatherings. People typically dress in traditional yukata (summer kimonos), bringing snacks and mats, and arrive early at riverbanks, parks, beaches, or lakesides to secure the perfect spot. As night falls and the first firework lights up the sky, cheers ripple through the crowd, and the air fills with excitement. The fireworks bloom in various colors and intricate shapes—circular bursts, heart shapes, cascading “waterfalls,” and even depictions of beloved characters, creating a mesmerizing visual experience.
Japanese fireworks artistry is renowned for its precision and innovation. Pyrotechnicians meticulously design each firework’s color, shape, and timing, ensuring that every show is unique. Many festivals even synchronize fireworks to music, creating a dynamic visual and auditory experience for the audience. Shows often consist of multiple chapters, each with distinct themes and color schemes, conveying different emotions and aesthetics throughout the event.
Among Japan’s many fireworks festivals, Tokyo’s Sumida River Fireworks Festival, Osaka’s Tenjin Matsuri Fireworks Festival, and the Nagaoka Fireworks Festival in Niigata are celebrated as Japan’s “Big Three” fireworks displays. The Sumida River festival is one of the oldest, with roots reaching back centuries, and is held along Tokyo’s Sumida River. Osaka’s Tenjin Matsuri combines fireworks with traditional Shinto rites, representing the Kansai region’s vibrant summer culture. Nagaoka’s Fireworks Festival, meanwhile, stands out for its dedication to peace and commemoration, delivering one of the country’s most awe-inspiring displays. Other popular fireworks events include Yokohama’s in Kanagawa, Noboribetsu in Hokkaido, and various festivals throughout regions, each with its unique ambiance and style.
For Japanese people, fireworks are a cherished tradition that embodies a deep respect for fleeting beauty. The brief, brilliant burst of fireworks symbolizes an appreciation for the momentary, a value deeply rooted in Japanese aesthetics. Each fireworks festival is more than a simple event—it’s a display of heritage and innovation, with each new year’s festival bringing fresh designs and artistic expression. Japanese pyrotechnicians pass down their skills through generations, preserving traditional beauty while constantly innovating to offer audiences something new and exciting each summer.
In conclusion, Japan’s fireworks festivals are a blend of beauty, tradition, and shared experience, making them a quintessential part of Japanese culture. For tourists, these festivals offer a chance to immerse themselves in Japanese summer traditions; for locals, they are a time to enjoy a cherished cultural event. With every burst of light and color in the sky, Japan’s fireworks festivals evoke a sense of nostalgia, joy, and hope—a reminder of the beauty of life’s fleeting moments.